This is used to add security to your web while transmitting the user information between server and client(browser).This is done by Encryption of data between server and client. If the browser identifies the Encryption and the certificate associated to it as trusted then it tells your user the connection is secure, you can transfer your personal information. You can handle your own certificate or use the certificate provided by third party Let’s Encrypt. Let us dive into let’sencrypt and open blackbox. It provides certificate for you in two methods.
Shell access(SSH access)
If you have Shell axis means you have ssh access to the server by the provider(Ex:AWS Ec2 instance). In that case it asks to have Certbot install in your server which automates the certificate issuance for you.Follow the steps mentioned in the Cerbot site to genetare a certificate which goes with the following process. Cerbot on your server generates the CSR (Certificate Signing Request).This process creates the private_key,public_key generated and sends the CSR data file which contains the public_key. The CA authority from CSR data creates a datastructure to match your private_key (never known to anyone including CA)and sends to your server .When once your server decodes it using private_key and sends acknoledgement to Let’s Encrypt. It generates the user certificate, issuer certificate which are stored in your server. So, we have generated the certificate, see working in Working section.
With out Shell access
If you don’t have shell access provided by your provider(Ex:Godaddy Hosting), then your hosting provider may give you access to manage your certificate(SSL/TSL).From the service provider (Godaddy) generate the private_key,CSR which generates the public_key and sends to the CA(Let’sEncrypt). The CA makes the datastructure frm CSR data and sends the some key files to you. You have to manully place them in the well defined location and CA authority tries to access them and if success then certificate is generated for you assuming you have the domain access. Use the certificates in your SSL panel and get secure your web. Follow the procedure in zerossl to get easily certified.
Working
When a browser attempts to access a website that is secured by SSL, the browser and the web server establish an SSL connection using a process called an “SSL Handshake” (see diagram below). Note that the SSL Handshake is invisible to the user and happens instantaneously. Essentially, three keys are used to set up the SSL connection: the public, private, and session keys. Anything encrypted with the public key can only be decrypted with the private key, and vice versa. Because encrypting and decrypting with private and public key takes a lot of processing power, they are only used during the SSL Handshake to create a symmetric session key. After the secure connection is made, the session key is used to encrypt all transmitted data.
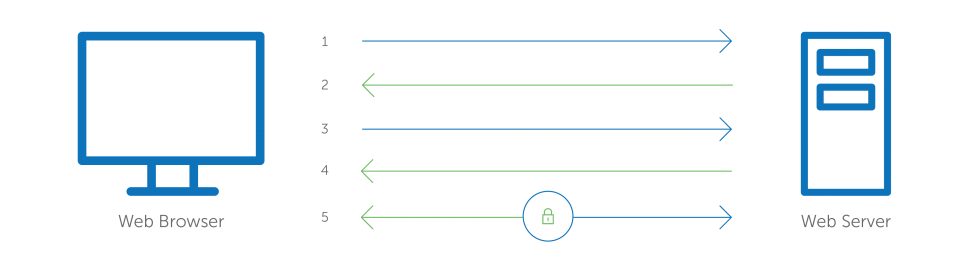 ;
;
- Browser connects to a web server (website) secured with SSL (https). Browser requests that the server identify itself.
- Server sends a copy of its SSL Certificate, including the server’s public key.
- Browser checks the certificate root against a list of trusted CAs and that the certificate is unexpired, unrevoked, and that its common name is valid for the website that it is connecting to. If the browser trusts the certificate, it creates, encrypts, and sends back a symmetric session key using the server’s public key.
- Server decrypts the symmetric session key using its private key and sends back an acknowledgement encrypted with the session key to start the encrypted session.
- Server and Browser now encrypt all transmitted data with the session key.
Comments powered by Disqus.